Search This Blog
This blog is designed to help those who would like to set up a working HACCP Program for a warehouse.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Storage Procedure for Food Warehouses
Keywords
Prerequisite Programs
Activities or conditions that are necessary to maintain food safety along the food chain.
First Expiry First Out(FEFO)
The inventory management system used to control the stock-flow based on expiry dates.
Storage is a vital element of the warehouse HACCP
program, and in most cases, cold storage is one of the CCPs (It can be a critical point or a CCP depending on the warehouse's risk assessment). If done wrong, it
could cause product deterioration because of the flourishment of spoilage
microorganisms like psychrophilic spoilage bacteria, which sometimes can be pathogenic. The
storage procedure details handling of received products and the documents
involved.
Proper storage involves a lot of inter-linking
activities aimed at protecting food products while at the warehouse. Some of
these are Pre-requisite Programs (PRPs) that support storage as a Critical
Control Point (CCP). They include the following;
- Cleaning and sanitation
- Temperature and humidity monitoring
- Pest control
- Inventory management
After receiving a food product, store it in an
appropriate environment, as instructed by the manufacturer. Storage instructions
are on the product’s labeling.
There are a lot of factors that dictate where the
product is stored. The storage procedure shows how products are handled in
line with these factors. They include the following;
- The nature of the product
- The ingredients
- Weight of the product
- Purpose of the product
- Date of expiry
Nature of the product
Food Products (dry, chilled, and frozen products)
To minimize product deterioration as a result of microbial spoilage store food products at 1-4 degrees Celsius for chilled products and -18 degrees Celsius (maximum -12°C) for frozen products. The warehouse storage procedure indicates the frequency of temperature monitoring (check product temperature at least twice a day), the person responsible, and whether it’s the product temperature or storage room temperature that is monitored.
Note:
- Temperature is measured using a calibrated
thermometer.
- The minimum frequency of temperature
monitoring is twice a day.
- A designated person must be trained in food safety and handling.
Proper segregation of unlike products should be
clear. Meat products, poultry products like eggs, and dairy products are
segregated from the rest of the products because they are Potentially Hazardous Foods (PHF). The purpose is to prevent
cross-contamination between products.
Proper segregation includes:
- Using separate racks.
- Using separate cold storage units.
- Using separate shelves on the same rack.
Ingredients
Take care when handling goods with allergen
ingredients. These are kept on separate bottom shelves and with a label. The
purpose of this is to distinguish them from the rest of the products. Proper
handling of allergens is vital to avoid contamination of other products and
their effects on consumers. We shall look at the allergen Policy in our
subsequent blogs.
Products containing high amounts of protein like
chicken products are separated from the rest by leaving at least two pallet
space (one on either side of the products) between protein products and the
rest of the products. They are also stored at the lower shelves to avoid
dripping, which would contaminate other products.
Date of expiry
Store products following FEFO (First Expiry First
Out) or FIFO (First In First Out). Put those that expire first on lower shelves
and those that expire last on the upper shelves of the racks. The reason is
simple - make those expiring first easy to access, and the opposite for
those expiring last. The intention is to minimize product expiration while at
the warehouse. Alternatively, color code the products for easy identification,
for instance, Blue for the first expiry, Green for the second expire, and
Orange for the last expiry.
Note
- All products are stored at 46cm from the wall to allow inspection and easy access during cleaning.
- The products are placed on clean and well-maintained pallets. Inspect for spikes in case you are using wooden pallets because they can damage the products, thus leading to spillage. The HACCP program must detail the cleaning and fumigation of pallets used in the warehouse.
- Avoid over stacking of products as this can damage the products.
Inventory management
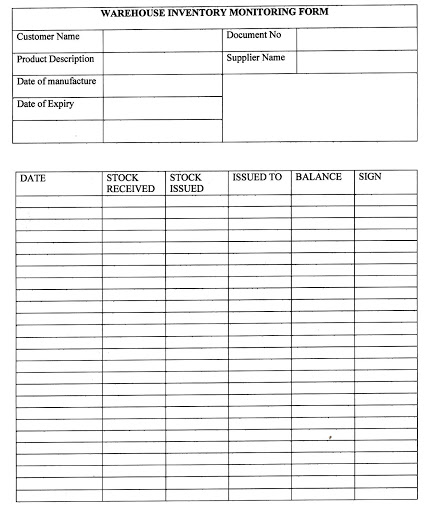
For proper management of the inventory, the
warehouse must have an inventory card/form for each product showing the amount
that was received; the amount issued out, the amount remaining on the shelves, and other product essential details used in case of a product recall. Appendix 1 shows a sample of a warehouse inventory form.
Storage of non-food products
In case the warehouse keeps other products like glass, cleaning chemicals, cleaning wares, these are stored in a demarcated area away from the food products. Special attention is given to glass materials because of the danger associated with them. Glassware is recorded and monitored in the Glass monitoring form and stored at the lower shelves such that in case of breakage, they don’t contaminate other products nearby.
Note:
- The storage areas must be kept clean by following the master cleaning schedule, which details the methods,
frequency, and chemicals used in the cleaning procedure.
- Each storage area must have a designated non-conforming area used to separate deviant products from the rest.
- Storage areas should be free of any pest infestation.
Corrective actions
Corrective
actions include; placing the deviant product on hold while waiting for a final decision by the warehouse management.
- Rejecting the non-conforming product and labeling it as a deviant product.
- Transferring products from a deviant storage unit.
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
or reload the browser
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Popular Posts
HACCP Program for Warehouse Handling Food Products- A simple Guide for Startups
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
.png)

I would like to thank you for the efforts you have made in writing this article.
ReplyDeletebulk powder whey protein
Thanks a lot William
ReplyDeletebetter get a cold management services offered by 3PL companies
ReplyDeletenice article I hope you can post more about cold storage management services
ReplyDeleteThank you Thea, I will soon publish more in-depth articles
ReplyDelete